Year 12 Common Module Study Guides
Learning methods available
Select a year to see available courses
The 2021 HSC Maths Std 2 Exam was on Monday 15 November. Read on to see how our Maths gurus would have answered things.

Join 75,893 students who already have a head start.
"*" indicates required fields
The Matrix 2021 HSC Maths Standard 2 Exam Paper Solutions are here!
Have you seen the 2021 HSC Mathematics Standard 2 exam Paper yet?
In this post, we will work our way through the 2021 HSC Maths Standard 2 exam paper and give you the solutions, written by our Head of Mathematics Oak Ukrit and his team.
| Question | Answer | Explanation |
| 1 | A | For option A, the perimeter is \(4 \times 8 = 32\) cm. For option B, the perimeter is \(2 \left(3 + 11\right) = 28\) cm. For option C, the perimeter is \(3 \times 10 = 30\) cm. For option D, the perimeter is \(3 + 4 + 4 + 9 = 20\) cm. |
| 2 | D | Vertex A has degree 4, vertex B is degree 3, vertex C has degree 4, vertex D has degree 2, and vertex E has degree 3. So the sum of the degrees of all the vertices is \(4 + 3 + 4 + 2 + 3 = 16\). |
| 3 | C | \(25\) appears twice, all the others appear once only, so the mode is \(25\). |
| 4 | D | Its salvage value is
\begin{align*} |
| 5 | B | His hourly wage after four years will be \begin{equation*} \$21.50 \left(1 + \frac{0.021}{1}\right)^{1 \times 4} = \$21.50 \times \left(1.021\right)^4 \end{equation*} |
| 6 | A | \begin{align*} a &= \frac{22}{7} \\ &= 3.14285 \dots \\ &= 3.14 \end{align*} |
| 7 | C | Options A and D show that there are close to 100 downloads on day 1, which is not consistent with the graph given, so they are wrong.
The graph given shows that the number of downloads increases from day 1 to day 10, and it decreases after that. Option B shows that the number of downloads every day is roughly the same, and that is inconsistent with the graph given. The graph in option C is consistent with all the features shown in the graph given. |
| 8 | D | \begin{align*} z &= \frac{x – \mu}{\sigma} \\ 2 &= \frac{x – 63}{8} \\ 16 &= x – 63 \\ x &= 79 \end{align*} |
| 9 | C | After subtracting \(8\) from the number, we get \(x – 8\). After multiply the result by \(3\), we get \(3 \left(x – 8\right)\).\(2\) more than \(x\) is \(x + 2\).
Since these two results are the same, we obtain \begin{equation*} |
| 10 | A | When \(x = 0\),\begin{align*} y &= 10 \left(0.8\right)^0 \\ &= 10 \left(1\right) \\ &= 10 \end{align*} so options B and D are wrong.Since \(0.8 < 1\), \(y = 10 \left(0.8\right)^x\) decreases as \(x\) increases, which means that option A is correct. |
| 11 | D | The probability that Kim and Sam choose chocolates with different centres is
\begin{align*} |
| 12 | B | 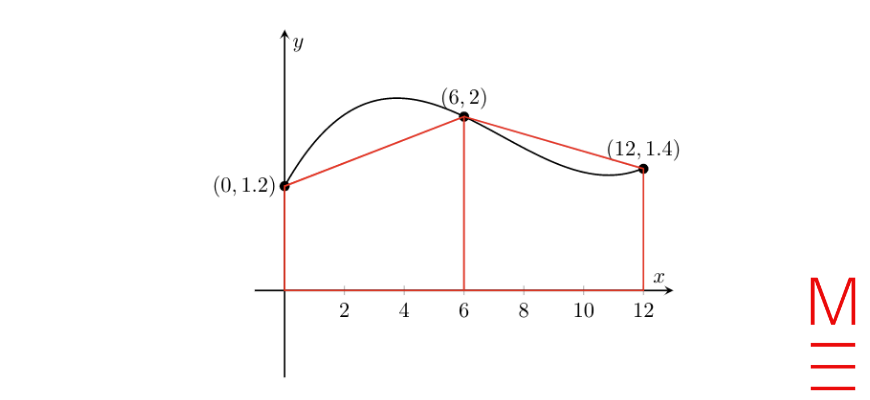
\begin{align*} |
| 13 | B | Let \(C\) be the number of cleaners, $t$ be the amount of time (in hours) it takes to clean the warehouse, and [/altex]k[/latex] be a constant. Then
\begin{align*} \begin{equation*} |
| 14 | D | 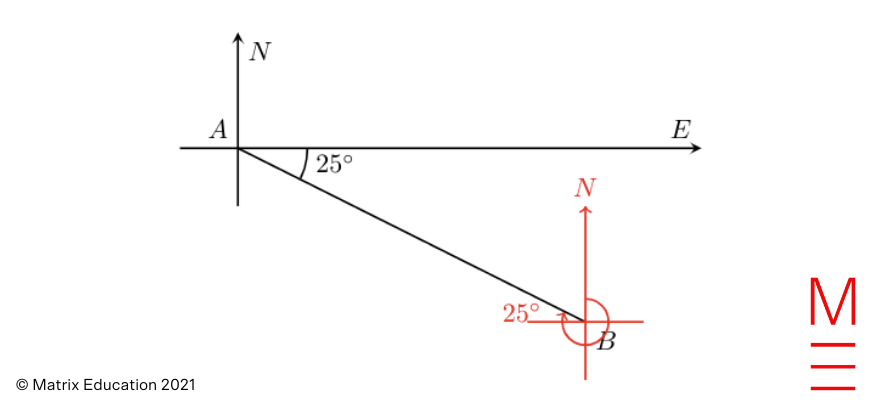
Since \(270^\circ + 25^\circ = 295^\circ\), the true bearing of \(A\) from \(B\) is \(295^\circ\). |
| 15 | B | \begin{align*}\text{number of professional runners} &= 11400 \times \frac{3}{3 + 16} \\ &= 1800 \end{align*} and \begin{align*} \text{total number of amateurs} &= 11400 \times \frac{16}{3 + 16} \\ &= 9600 \end{align*}Also, \begin{align*} \text{number of amateurs who completed the race} &= 9600 – 600 \\ &= 9000 \end{align*}So, \begin{align*} \text{no.\ of professional runners who completed the race} : \text{no.\ of amateurs who completed the race} &= 1800 : 9000 \\ &= 1 : 5 \end{align*} |
Learn to solve any Maths question! Expert teachers, weekly quizzes, one-to-one help! Ace your next Maths Std 2 assessment with Matrix+ Online.
| \begin{align*} V &= \frac{1}{2} \times \left[\frac{4}{3} \pi \left(2\right)^3\right] \\ &= 16.75516082 \\ &= 16.8 \; \text{cm}^3 \quad \text{(1 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{IQR} &= Q_3 – Q_1 \\ &= 10 – 4 \\ &= 6 \end{align*}and\begin{align*} Q_3 + 1.5 \times IQR &= 10 + 1.5 \times 6 \\ &= 19 \end{align*}Since \(20 > 19\), it is an outlier. |
| \begin{align*} \text{amount of fuel used for the trip} &= 1560 \times \frac{6.7}{100} \\ &= 104.52 \, \text{L} \end{align*}\begin{align*} ∴ \text{total fuel cost for the trip} &= 104.52 \times 1.45 \\ &= \$151.55 \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} S &= V_0 – D_n \\ 7500 &= V_0 – 2300 \times 5 \\ V_0 &= 7500 + 2300 \times 5 \\ V_0 &= \$19000 \end{align*} |
We are only concerned about the longitude, i.e. how far East or West. Since \(151^\circ – 16^\circ = 135^\circ\),
| \begin{align*} \text{time difference} &= \frac{135^\circ}{15} \\ &= 9 \, \text{hours (Australia is earlier)} \end{align*}So Robert should start at 2AM on Friday. |
| \begin{align*} \text{interest rate} &= \frac{18.75}{12500} \\ &= 0.0015 \\ &= 0.15 \% \end{align*}In month 7,\begin{align*} \text{monthly interest} &= \$15624.20 \times 0.0015 \\ &= \$23.44 \end{align*}and\begin{align*} \text{amount at the end of month 7} &= \$15624.2 + \$23.44 + \$500 \\ &= \$16147.64 \end{align*}So the final row of the table is as follows:
|
| \begin{align*} \text{Taxable income } &= 84000 – 900 – 474 \\ &= 82626 \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{Income tax } &= 5092 + 0.325 \times (82626 – 45000) \\ &= 17320.45 \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{Medicare Levy } &= 82626 \times 0.02 \\ &= 1652.52 \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{Total tax payable } &= 17320.45 + 1652.52 \\ &= \$ 18972.97 \end{align*} |
The minimum spanning tree is
| The fastest route is Queenstown \(\rightarrow\) Minertown \(\rightarrow\) Underwood, so
\begin{align*} |
| When \(t = 0\),
\begin{align*} |
| When \(t = 5\),
\begin{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{perimeter} &= 2 \left(5 + 8\right) \\ &= 26 \, \text{cm} \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{distance travelled} &= 26 \times 3000 \\ &= 78000 \, \text{cm} \\ &= 780 \, \text{m} \\ &= 0.78 \, \text{km} \end{align*}Also,\begin{align*} 12 \, \text{minutes} &= \frac{12}{60} \, \text{hour} \\ &= \frac{1}{5} \, \text{hour} \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{average speed} &= \frac{0.78 \, \text{km}}{\frac{1}{5} \, \text{hour}} \\ &= 0.78 \times 5 \\ &= 3.9 \, \text{km/hour} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{FV} &= \text{PV} \left(1 + r\right)^n \\ &= 35000 \left(1 + \frac{0.06}{12}\right)^{12} \\ &= \$37158.72 \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{FV} &= \text{PV} + \text{I} \quad \text{(simple interest)} \\ \text{FV} &= \text{PV} + Prt \\ 37158.72 &= 35000 + 35000 \times r \times 1 \\ 2158.72 &= 35000r \\ r &= \frac{2158.72}{35000} \\ r &= 0.06167 \dots \\ r &= 6.17 \% \text{( 2 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
| For Television B,
\begin{align*} and \begin{align*} so \begin{align*} |
| Let \(n\) be the number of years it will take.
\begin{align*} So it will take 5 years. |
Set calculator to STAT mode, select “A + Bx” and enter data points into table.
The \(y\)-intercept is \(2\) and the gradient is \(3.2\).
Hence, the equation of the least-squares regression line is \(y = 3.2 x + 2\);
The data point (10,45) would be above the regression line in the diagram, so the gradient would increase.
Question 29
| \begin{align*} x + \frac{x – 1}{2} &= 9 \\ \frac{2x + x – 1}{2} &= 9 \\ 3x – 1 &= 18 \\ 3x &= 19 \\ x &= \frac{19}{3} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{dividend yield} &= \frac{810}{1500 \times 27} \\ &= 0.02 \\ &= 2\% \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} r = \frac{1.5}{12} = 0.125\% \\ N = 30\times12 = 360 \\ PV = \frac{500000}{289.75411} = \$1725.60 \text{ Monthly}\\ \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \cos 30^\circ &= \frac{XY}{16} \\ XY &= 16 \cos 30^\circ \\ XY &= 13.86 \, \text{cm} \quad \text{(2 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \text{Area of semicircle} &= \frac{1}{2} \times \pi(8)^2 \\ &= 32\pi \; \text{cm}^2 \end{align*}Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can complete the triangle as |
| \begin{align*} \text{Area of triangle} &= \frac{1}{2}(8)(8 \sqrt{3}) \\ &= 32 \sqrt{3} \; \text{cm}^2 \end{align*}\begin{align*} \text{Total area of shaded region} &= \text{Area of semicircle} – \text{Area of triangle} \\ &= 32 \pi – 32 \sqrt{3} \\ &\approx 45.1 \; \text{cm}^2 \quad \text{(1 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
(i)
| \begin{align*} y &= 29.2 – 0.011 \times 540 \\ &= 23.3^\circ \, \text{C} \quad \text{(1 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
(ii)
As the height above sea level increases, the average maximum daily temperature decreases since the gradient of the regression line is negative.
Latitude would be a better predictor as the magnitude of the correlation coefficient is greater (\(-0.897\) compared to \(-0.494\)). This indicates a stronger linear relationship between the two variables.
We can formulate the statement “In total the emus and goannas have 76 legs”, as
\begin{equation*}
4x + 2y = 76 \,,
\end{equation*}
which dividing both sides by \(2\) gives
\begin{equation}
2x + y = 38 \tag{1}
\end{equation}
We are given that
\begin{equation}
x + y = 31 \tag{2}
\end{equation}
So \(\text{Eq.}(1) – \text{Eq.}(2)\) gives
\begin{equation*}
x = 7
\end{equation*}
Substituting \(x = 7\) into Eq.(2) gives
\begin{align*}
7 + y &= 31 \\
y &= 24
\end{align*}
Therefore, there are 7 goannas and 24 emus.
| The revenue is maximised when \(x\) is the midpoint between \(x = -10\) and \(x = 100\), which is
\begin{align*} \begin{align*} |
| When\(x = 0\),
\begin{align*} so the intercept of the parabola with the vertical axis is \(50000\). |
40 minutes.
ACDEGJK
| \begin{align*} \text{Float time} &= \text{LST} – \text{EST} \\ &= 18 – 17 \\ &= 1 \; \text{minute} \end{align*} |
| Using the sine law,
\begin{align*} For \(obtuse \angle ABC\), it is \(180^\circ – 47^\circ = 133^\circ\). |
| \begin{align*} P \left(Z > 0.3\right) &= P \left(Z > 0\right) – P \left(0 \leq Z \leq 0.3\right) \\ &= 0.5 – 0.1179 \\ &= 0.3821 \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} z &= \frac{x – \mu}{\sigma} \\ &= \frac{3471 – 3300}{570} \\ &= 0.3 \end{align*}\begin{align*} ∴ \text{expected number of babies who have a birth weight greater than 3471 grams} &= 0.3821 \times 1000 \\ &= 382 \quad \text{(nearest whole baby)} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} A &= \frac{1}{2} ab \sin C \\ 466 &= \frac{1}{2} \left(28\right) \left(35\right) \sin \angle COB \\ \sin \angle COB &= \frac{233}{245} \\ \angle COB &= \sin^{-1} \left(\frac{233}{245}\right) \\ \angle COB &= 72^\circ \quad \text{(nearest degree)} \end{align*} |
| \begin{align*} \angle DOC &= 330^\circ – 150^\circ – 72^\circ \\ &= 108^\circ \end{align*}By the cosine rule,\begin{align*} DC^2 &= 31^2 + 28^2 – 2 \left(31\right) \left(28\right) \cos 108^\circ \\ DC^2 &= 2281.45 \\ DC &= \sqrt{2281.45} \\ DC &= 47.8 \, \text{m} \end{align*}So\begin{align*} \text{length of fencing required} &= 31 + 28 + 47.8 \\ &= 106.8 \, \text{m} \quad \text{(1 d.p.)} \end{align*} |
| The PV is \(1000\) and the interest factor is \(8.2132\), so
\begin{align*} at the end of 8 years, and \begin{align*} at the end of 10 years. |
Let \(X\) be a female’s height in the population and \(Y\) be a male’s height.
\begin{align*}
P(X< 175) &= 97.5\% \\
P(X < 160.6) &= 16\% \\
P(Y < h) &= 84\%
\end{align*}
Our aim is the find \(h\). Use the empirical rule with the information given above.
\begin{align*}
\mu + 2\sigma &= 175 & \text{(1)} \\
\mu – \sigma &= 160.6 & \text{(2)}
\end{align*}
Subtracting equation (1) by (2) gives
\begin{align*}
3 \sigma &= 14.4 \\
∴ \sigma &= 4.8
\end{align*}
Substitute \(\sigma = 4.8\) into (1),
\begin{align*}
\mu + 2(4.8) &= 175 \\
\mu = 165.4
\end{align*}
Hence, for the adult male population, the mean is \(1.05 \mu = 173.67\) and the standard deviation is \(1.1 \sigma = 5.28\).
Since being 84 % taller than the male population is 1 standard deviation above the mean, then we can calculate \(h\) as
\begin{align*}
h &= 1.05 \mu + 1.1 \sigma \\
&= 173.67 + 5.28 \\
&= 178.95 \; \text{cm}
\end{align*}
Written by Matrix Maths Team
The Matrix Maths Team are tutors and teachers with a passion for Mathematics and a dedication to seeing Matrix Students achieving their academic goals.© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2023. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.