Welcome to Matrix Education
To ensure we are showing you the most relevant content, please select your location below.
Select a year to see courses
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Learn online or on-campus during the term or school holidays
Select a year to see available courses
Science guides to help you get ahead
Science guides to help you get ahead
It's time to level up your text analysis skills. Learn how to analyse symbolism in literature and uncover what’s really being said.

Join 75,893 students who already have a head start.
"*" indicates required fields
You might also like
Related courses

Join 8000+ students each term who already have a head start on their school academic journey.
There’s more to literature than the stories and characters; it’s often about the ideas hidden beneath them. One of the ways authors add depth to their writing is through the artistic use of symbolism. This means using objects, colours or settings to represent something bigger.
Here’s everything you need to know to analyse symbolism in literature and write stronger responses in English class.
Table of contents:
Symbolism is when authors use something like an object, colour, action, or setting to represent a deeper idea or concept. It’s a powerful way to add meaning without spelling everything out.
For example:
These symbols aren’t always obvious, but they help readers understand the emotional or thematic layers of a text. Once you learn to spot them, you’ll see how authors use symbolism to connect ideas, build tension, and reveal key literary themes.
Symbolism is when something (an object, colour, or setting) stands for more than just what it is.
Symbolism helps authors say more with less. Here’s how it’s used to add meaning to a story.
Symbols help express big ideas without explaining them directly. In F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby, the green light at the end of Daisy’s dock symbolises Gatsby’s unreachable hopes and dreams. It shows how some goals (like the American dream) can feel just out of reach, showing the gap between desires and reality.
Symbols can also tell us more about characters and their values. In To Kill a Mockingbird, the mockingbird is a symbol for innocence. It reminds us that it’s wrong to harm people who haven’t done anything wrong, like Tom Robinson. This symbol helps us see how Scout and Jem grow and understand the world around them.
Sometimes, a place or object in a story helps create a certain feeling. So, settings can be full of symbolism. The decaying state of the house in Edgar Allan Poe’s The Fall of the House of Usher symbolises the deteriorating mental state of the people living inside it. The crumbling structure is a physical manifestation of the family’s decline. In other words, the setting adds to the eerie, sad mood of the story.
Authors use symbols to connect with emotions we already have. These emotions are often tied to personal and cultural contexts. For example, white is frequently associated with purity and peace; however, in some cultures, it can signify mourning (as seen in various Asian traditions). Authors use these emotional links to make stories more powerful and relatable.
Understanding symbolism is just the start. Knowing how to write about it clearly is what gets top marks. Matrix English experts teach these exact techniques in structured term courses.
HSC writing strategies from expert English teachers
Band 6 resources to get you exam-ready. Join the 96% of our students that have improved their marks.
You can identify symbols by looking for objects, actions, or themes that appear repeatedly or seem to carry more weight than their literal meaning.
Symbols can seem tricky at first, but with a bit of practice, you’ll start to notice them more easily. Here’s how to spot and understand them:
Learning to spot symbolism can help you understand the theme more clearly and make your English responses stand out.
Seeing symbols is sometimes easier than reading them. Start analysing symbols in film by downloading our free Film Analysis Planner. Organise your ideas, develop deeper insights, and sharpen your essay responses.
Improve your analysis with templates, study prompts, and essay tips! Fill out your details below to get this resource emailed to you. "*" indicates required fields
Download your free Film Analysis Planner

Download your free Film Analysis Planner
Symbols don’t always mean the same thing to everyone. Their meaning can change based on culture, time, or personal experiences. For example:
To understand symbols in a story, pay attention to how they’re used, how often they appear, and how they make people feel. Knowing the cultural and historical background can also help you see the deeper meaning behind them.
1. The whale in Moby-Dick
The giant white whale isn’t just a whale — it symbolises obsession and the dangers of chasing something too hard. It also reflects the struggle between humans and nature, or the idea of fighting fate.
2. The green light in The Great Gatsby
The green light at the end of Daisy’s dock symbolises Jay Gatsby’s aspirations and the elusive nature of the American Dream. It embodies hope, desire, and the inevitable disillusionment that comes with chasing idealised goals.
3. The scarlet letter in The Scarlet Letter
At first, the letter “A” symbolises sin, shame, and social ostracism. But it evolves into a representation of strength and resilience. This transformation invites you to explore themes of redemption and personal growth even in the face of society’s judgment.
4. The mockingbird in To Kill a Mockingbird
The mockingbird is a powerful symbol of innocence and the moral obligation to protect those who do not deserve harm. Killing the Mockingbird is a metaphor for injustice inflicted upon the innocent, underscoring themes of morality and human dignity.
5. Big Brother in 1984
George Orwell uses Big Brother to symbolise oppressive government surveillance. It shows what life could be like without freedom or privacy under a harsh and controlling system.
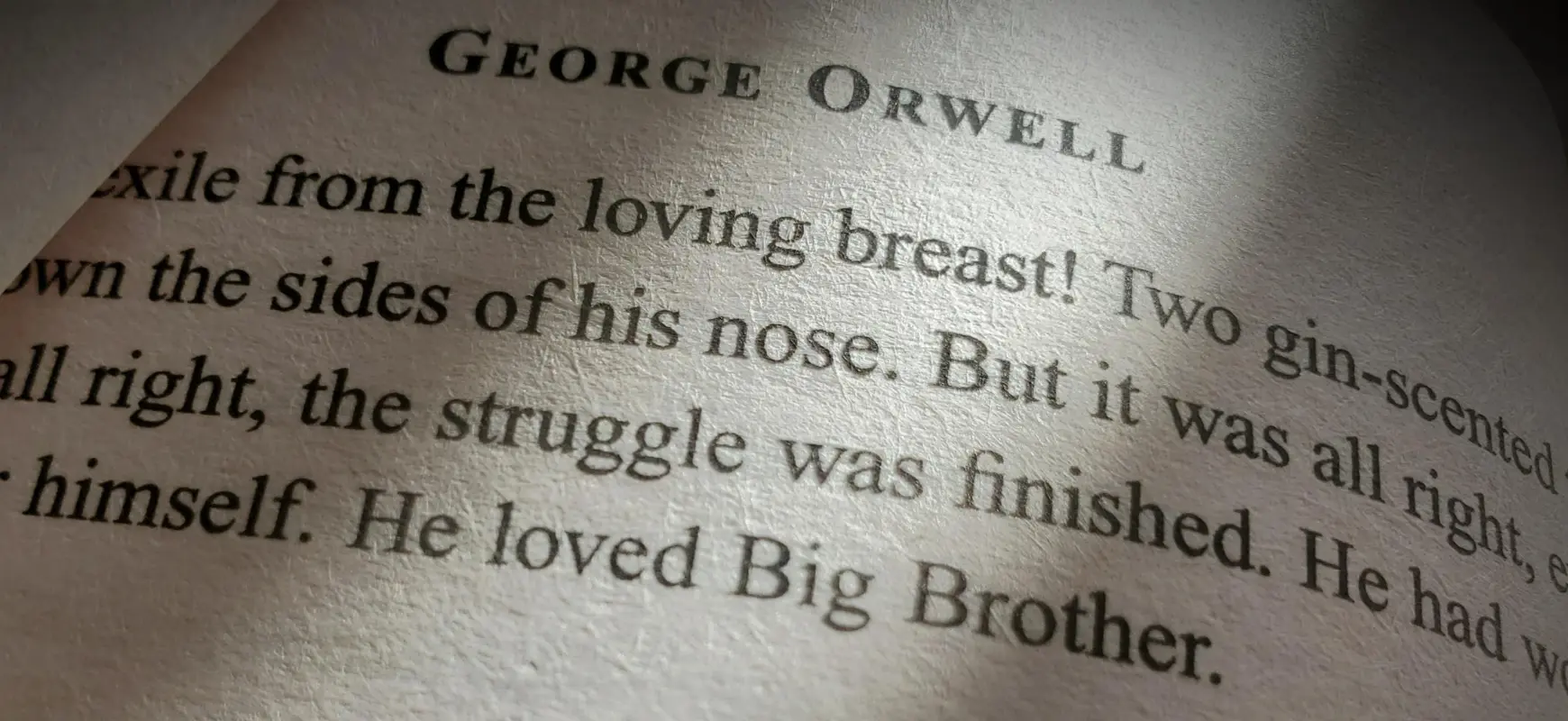
In modern stories, authors still use symbols to add deeper meaning. Here are a few examples:
1. The mockingjay in The Hunger Games (Suzanne Collins)
2. The road in The Road (Cormac McCarthy)
3. The house in The House on Mango Street (Sandra Cisneros)
Symbols help stories say more than what’s written. These carefully selected symbols add meaning and help us think more deeply about the characters, their choices, and the world around them. When you read, keep an eye out for repeated images, objects, or actions — they often tell a bigger story beneath the surface.
It takes practice to analyse symbolism in literature. With the right support, it becomes second nature.
Matrix English students build these skills every week through structured lessons, exam-style practice, and expert feedback.
Boost your HSC English Advanced marks!
Expert teachers, detailed feedback, and 1-to-1 support to help you excel. Book your free trial today.
Written by Matrix English Team
The Matrix English Team are tutors and teachers with a passion for English and writing, and a dedication to seeing Matrix Students achieving their academic goals.© Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au, 2025. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Matrix Education and www.matrix.edu.au with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.